| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
- var
- 재귀함수
- AWS조사
- 스코프
- complexity
- 코드스테이츠
- 메모이제이션
- AWS
- 리커젼
- IT
- node.js
- prototype
- 생활코딩
- appendChild
- 기초공부
- node.js설치
- vscode
- css기초
- APPEND
- let
- 인터프리터
- AWS기초
- Big-O notation
- 클로저
- JavaScript
- 개발툴
- scope
- CSS
- 원본과 복사본
- flex기본
- Today
- Total
Jveloper
스택과 큐, linked list 본문
스택이란?

● 스택의연산
- 스택의 pop함수를 이용하여 빼내면 1이 먼저 나오는것이 아닌 5가 먼저 나오게된다
- 스택은 같은 방향에서 아이템을 추가하고 삭제한다는 조건하에 연결리스트로도 구현이 가능하다
● 스택의 추상 데이터타입(ADT) (-> 단순하게 생각해서 쉽게 해결하기 위해 추상적으로 내가 정의한 코드라고 이해할 수 있을것같다 )
- pop() : 스택에서 가장 위에있는 항목을 제거함
- push(item) : item 하나를 스택의 가장 윗부분에 추가함
- peek() : 스택의 가장 위에있는 항목을 반환함
- isEmpty() : 스택이 비어있을때에 true를 반환함
● 스택의 활용사례
1. 재귀 알고리즘
- 재귀적으로 함수를 호출해야 하는 경우에 임시 데이터를 스택에 넣어준다.
- 재귀함수를 빠져 나와 퇴각 검색(backtrack)을 할 때는 스택에 넣어 두었던 임시 데이터를 빼 줘야 한다.
- 스택은 이런 일련의 행위를 직관적으로 가능하게 해 준다.
- 또한 스택은 재귀 알고리즘을 반복적 형태(iterative)를 통해서 구현할 수 있게 해준다.
2. 웹 브라우저 방문기록 (뒤로가기)
3. 실행 취소 (undo)
4. 역순 문자열 만들기
● 의사코드(스택의 크기는 5로 가정한다)
function Stack(){
let items = [];
this.push = function(ele){
if(items.length > 5){
console.log("full stack");
} else {
items.push(ele);
}
}
this.pop = function(){
if(items.length <= 0){
console.log("empty stack");
} else {
items.pop();
}
}
this.peek = function(){
return items[items.length - 1];
}
this.isEmpty = function(){
if(items.length === 0 ){
return true;
}
}
}class Stack{
constructor(){
this.items = [];
}
}
Stack.prototype.push = function(ele){
if(this.items.length > 5){
console.log("full stack");
} else {
this.items.push(ele);
}
}
Stack.prototype.pop = function(){
if(this.items.length <= 0){
console.log("empty stack");
} else {
this.items.pop();
}
}
Stack.prototype.peek = function(){
return this.items[this.items.length - 1];
}
Stack.prototype.isEmpty = function(){
if(this.items.length === 0){
return true;
}
}
let stack = new Stack();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
stack.push(5);
stack.push(6); // "full stack"
stack.peek(); // 5
큐란?

스택과 반대되는 개념
● 큐의 추상데이터타입
enQueue() = 큐에 아이템을 추가한다
deQueue() = 큐의 첫번째 항목을 제거한다
peek() = 큐 맨앞에 있는 요소를 반환한다.
isEmpty() = 큐가 비어 있는지를 검사한다.
isFull() = 큐가 가득 찼는지를 검사한다.
● 큐의 활용사례
- 우선순위가 같은 작업 예약 (인쇄 대기열)
- 선입선출이 필요한 대기열 (티켓 카운터)
- 콜센터 고객 대기시간
● 의사코드(큐의 크기는 5로 가정한다)
function Queue(){
let items = [];
this.enQueue = function(ele){
if(items.length >= 5){
console.log("full Queue");
} else {
items.push(ele)
}
}
this.deQueue = function(){
if(items.length <= 0){
console.log("empty Queue");
} else {
items.shift();
}
}
this.peek = function(){
return items[0];
}
this.isEmpty = function(){
if(items.length === 0){
return true;
}
}
this.isFull = function(){
if(items.length === 5){
return true;
}
}
}
class Queue{
constructor(){
this.items = [];
}
}
Queue.prototype.enQueue = function(ele){
if(this.items.length >= 5){
console.log("full Queue");
} else {
this.items.push(ele);
}
}
Queue.prototype.deQueue = function(){
if(this.items.length <= 0){
console.log("empty Queue");
} else {
this.items.shift(); // 앞에 들어온게 먼저 나가야하기 때문에 여기서는 shift를 쓴다.
}
}
Queue.prototype.peek = function(){
return this.items[0];
}
Queue.prototype.isEmpty = function(){
if(this.items.length === 0){
return true;
}
}
Queue.prototype.isFull = function(){
if(this.items.length === 5){
return true;
}
}
Linked list(연결리스트)란?
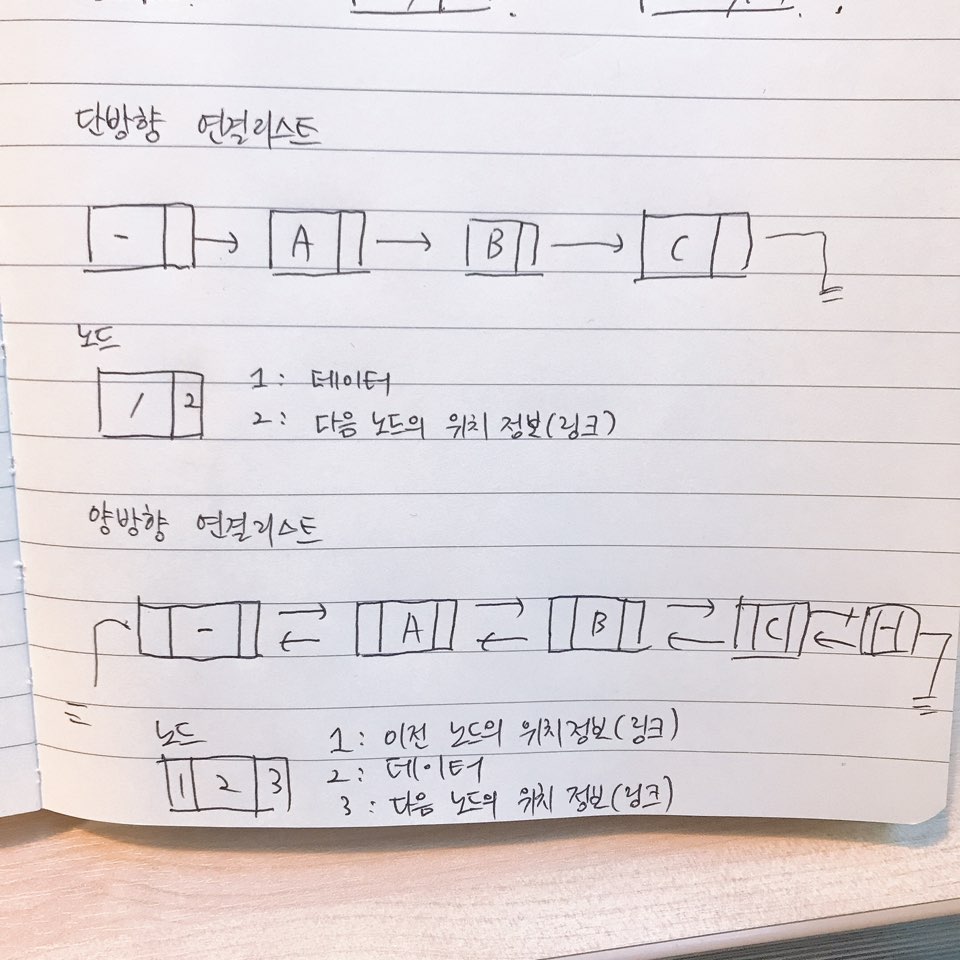
- 배열이 정적인 자료구조라면 연결리스트는 동적인 자료구조
- 필요하면 할당하고 필요없으면 삭제하는식의 메모리 관리가 가능 즉, 메모리 절약이 가능
- 최대 장점은 재배열이 쉽다는점, 자료의 순서를 바꾸려면 링크가 가리키는 방향만 바꾸어주면 됨
class Node{
constructor(element){
this.ele = element;
this.next = null;
}
}
class LinkedList{
constructor(){
this.head = new Node("head");
}
find(item){
let currNode = this.head;
while(currNode.element != item){
currNode = currNode.next;
}
return currNode;
}
insert(newElement, item){
let newNode = new Node(newElement);
let current = this.find(item);
newNode.next = current.next;
current.next = newNode;
}
display(){
let currNode = this.head;
while(!(currNode.next == null)){
console.log(currNode.next.element);
currNode = currNode.next;
}
}
findPrevious(item){
let currNode = this.head;
while(!(currNode.next == null) && (currNode.next.element != item)){
currNode = currNode.next;
}
return currNode;
}
remove(item){
let prevNode = this.findPrevious(item);
if(!(prevNode.next == null)){
prevNode.next = prevNode.next.next;
}
}
}
const 연결리스트 = new LinkedList();
연결리스트.insert("Seoul","start"); //start->Seoul
연결리스트.insert("Busan","Seoul"); //start->Seoul->Busan
연결리스트.insert("Daegu","Seoul"); //start->Seoul->Daegu->Busan
연결리스트.insert("Incheon","Busan"); //start->Seoul->Daegu->Busan->Incheon
연결리스트.display(); //start->Seoul->Daegu->Busan->Incheon
연결리스트.remove("Busan");
연결리스트.display(); //head->Seoul->Daegu->Incheon
class Node{
constructor(element){
this.element = element;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
class LinkedList{
constructor(){
this.head = new Node("start");
}
find(item){
let currNode = this.head;
while(currNode.element !== item){
currNode = currNode.next;
}
return currNode;
}
insert(newElement, item){
let newNode = new Node(newElement);
let current = this.find(item);
if(current.next === null){
newNode.next = null;
newNode.prev = current;
current.next = newNode;
} else {
newNode.next = current.next;
newNode.prev = current;
current.next.prev = newNode;
current.next = newNode;
}
}
display(){
let currNode = this.head;
while(!(currNode.next === null)){
console.log(currNode.next.element);
currNode = currNode.next;
}
}
remove(item){
let currNode = this.find(item);
if(!(currNode.next === null)){
currNode.prev.next = currNode.next;
currNode.next.prev = currNode.prev;
currNode.next = null;
currNode.prev = null;
}
}
findLast(){
let currNode = this.head;
while(!(currNode.next === null)){
currNode = currNode.next;
}
return currNode;
}
dispReverse(){
let currNode = this.head;
currNode = this.findLast();
while(!(currNode.prev === null)){
console.log(currNode.element);
currNode = currNode.prev;
}
}
}
const 양방향 = new LinkedList();
양방향.insert('apple', 'start'); // start->apple
양방향.insert('banana', 'apple'); // start->apple->banana
양방향.insert('cherry', 'apple'); // start->apple->cherry->banana : 양방향이라 바나나의 이전으로 넣는게 가능해짐
양방향.insert('apple', 'start'); // start->apple
'자료구조 > 시간복잡도 & 공간복잡도' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 힙(Heap) (0) | 2019.12.16 |
|---|---|
| 선형구조와 비선형구조(자료구조의 하위 카테고리) (0) | 2019.06.11 |
| 그래프, 트리, B-tree, 해쉬테이블 (0) | 2019.05.30 |
| Big-O notation (0) | 2019.05.07 |



